Here are some recent case studies that WIOMAX researchers and engineers have done on smart transportation and road safety studies.
Please contact us if you have questions and comments about our research, development, applications, and services, or would like to explore potential collaborations with us.SIV-DSS: Smart IoT (V2X) for Intersection Safety |
|---|
In this project, we have proposed an integrated in-vehicle decision support system to help driver make better and safer stop/go decisions as a vehicle is approaching a signalized intersection.
- “SIV-DSS: Smart in-vehicle decision support system for driving at signalized intersections with V2I communication,” Transportation Research Part C, vol. 90, 2018.
![[PDF]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/doi.png)
![[Bibtex]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/bib.png)
@Article{Xie2018SIV, Title = {{SIV-DSS}: Smart in-vehicle decision support system for driving at signalized intersections with {V2I} communication}, Author = {Xiao-Feng Xie and Zun-Jing Wang}, Journal = {Transportation Research Part C}, Volume = {90}, Pages = {181--197}, PDF={http://www.wiomax.com/team/xie/paper/TRC18Pre.pdf}, Doi = {10.1016/j.trc.2018.03.008}, Year = {2018} }
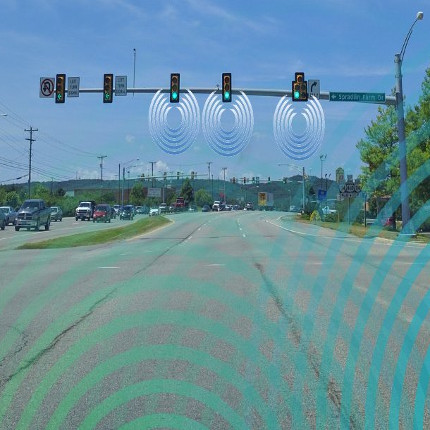 Supported by the IoT communications, the system has integrated and harnessed real-time information from both vehicle and infrastructure. Novel decision rules are designed as smart modules utilizing the key physical and behavioral inputs from vehicle motion, vehicle-driver characteristics, intersection geometry and topology, signal phase and timings, and the definition of red-light running (RLR) law. The performance has been evaluated with systematic simulation experiments. The results indicate that the smart system can not only ensure traffic safety by greatly reducing the probability of RLR violations down to zero, but also improve mobility by significantly reducing unnecessary stops at an intersection.
Supported by the IoT communications, the system has integrated and harnessed real-time information from both vehicle and infrastructure. Novel decision rules are designed as smart modules utilizing the key physical and behavioral inputs from vehicle motion, vehicle-driver characteristics, intersection geometry and topology, signal phase and timings, and the definition of red-light running (RLR) law. The performance has been evaluated with systematic simulation experiments. The results indicate that the smart system can not only ensure traffic safety by greatly reducing the probability of RLR violations down to zero, but also improve mobility by significantly reducing unnecessary stops at an intersection.
CTCRCO: Combined Traffic Control and Route Choice Optimization for Road Networks |
|---|
- “Combined traffic control and route choice optimization for traffic networks with disruptive changes,” Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics, vol. 7, iss. 1, 2019.
![[DOI]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/doi.png)
![[Bibtex]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/bib.png)
@Article{Xie2018RCTC2, Title = {Combined traffic control and route choice optimization for traffic networks with disruptive changes}, Author = {Xiao-Feng Xie and Zun-Jing Wang}, Journal = {Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics}, Volume = {7}, number={1}, Pages = {814-833}, Doi = {10.1080/21680566.2018.1517059}, Year = {2019} }
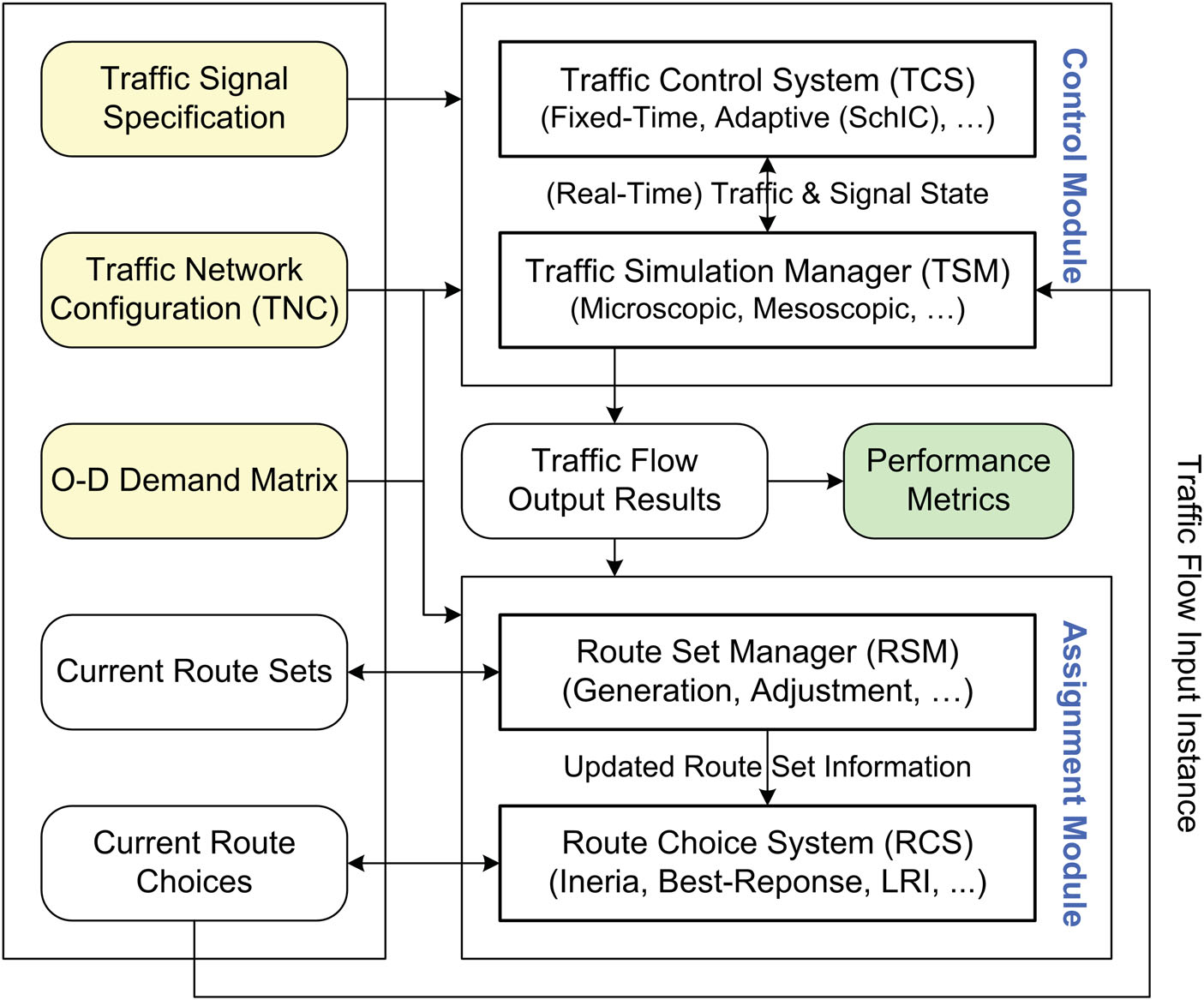 We present a combined traffic control and route choice optimization (CTCRCO) system to quickly find new traffic equilibrium solutions in urban road networks with significant changes. The system iteratively executes a control module which combines a traffic control system (TCS) and a traffic simulation manager (TSM) and an assignment module which combines a route set manager (RSM) and a route choice system (RCS), thus can optimize both traffic flows and route choices for minimizing average travel time of vehicles. We evaluate CTCRCO by testing various traffic scenarios in real-world road networks with significant changes. The results show that TCS and RCS are both significant for achieving a quick and low-cost convergence to an approximate equilibrium in a road network with significant changes. Approximate simulations not only accelerate convergence processes for non-congested cases, but also bypass potential gridlock states for over-congestion cases. The role of different path-finding procedures is also examined.
We present a combined traffic control and route choice optimization (CTCRCO) system to quickly find new traffic equilibrium solutions in urban road networks with significant changes. The system iteratively executes a control module which combines a traffic control system (TCS) and a traffic simulation manager (TSM) and an assignment module which combines a route set manager (RSM) and a route choice system (RCS), thus can optimize both traffic flows and route choices for minimizing average travel time of vehicles. We evaluate CTCRCO by testing various traffic scenarios in real-world road networks with significant changes. The results show that TCS and RCS are both significant for achieving a quick and low-cost convergence to an approximate equilibrium in a road network with significant changes. Approximate simulations not only accelerate convergence processes for non-congested cases, but also bypass potential gridlock states for over-congestion cases. The role of different path-finding procedures is also examined.
Data-Driven Decision Supports (DDDS): Bike Sharing Analysis: Washington DC |
|---|
Bikesharing has gradually become an adopted form of mobility in urban area recent years as one sustainable transportation mode to bring us many social, environmental, economic, and health-related benefits and rewards. There is increased research toward better understanding of bikesharing systems (BSS) in urban environments. However, our comprehension remains incomplete on the patterns and characteristics of BSS.
- “Examining travel patterns and characteristics in a bikesharing network and implications for data-driven decision supports: Case study in the Washington DC area,” Journal of Transport Geography, vol. 71, 2018.
![[PDF]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/doi.png)
![[Bibtex]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/bib.png)
@Article{Xie2018Bike, Title = {Examining travel patterns and characteristics in a bikesharing network and implications for data-driven decision supports: Case study in the {Washington DC} area}, Author = {Xiao-Feng Xie and Zun-Jing Wang}, Journal = {Journal of Transport Geography}, Volume = {71}, Pages = {84--102}, PDF={http://www.wiomax.com/team/xie/paper/JTRG18Pre.pdf}, Doi = {10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2018.07.010}, Year = {2018} }
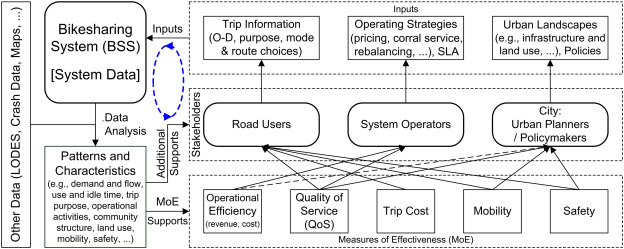 In this work, aiming to help improving sustainability in multimodal transportation through BSS, we perform a systematic data analysis to examine underlying patterns and characteristics of the system dynamics in a bikeshare network and to acquire implications of the patterns and characteristics for decision making. As a case study, we use trip history data from the Capital Bikeshare system in the Washington DC area and some additional data sources. The study covers seven important aspects of bikeshare transportation systems, which are respectively trip demand and flow, operating activities, use and idle times, trip purpose, origin-destination flows, mobility, and safety. For these aspects, by using appropriate statistical methods and geographic techniques, we investigate travel patterns and characteristics of BSS from data to evaluate the qualitative and quantitative impacts of the inputs from key stakeholders on main measures of effectiveness such as trip costs, mobility, safety, quality of service, and operational efficiency, where key stakeholders include road users, system operators, and city. We also disclose some new patterns and characteristics of BSS to advance the knowledge on travel behaviors. Finally, we briefly summarize our findings and discuss the implications of the patterns and characteristics for data-driven decision supports from the relations between BSS and key stakeholders for promoting bikeshare utilization and transforming urban transportation to be more sustainable.
In this work, aiming to help improving sustainability in multimodal transportation through BSS, we perform a systematic data analysis to examine underlying patterns and characteristics of the system dynamics in a bikeshare network and to acquire implications of the patterns and characteristics for decision making. As a case study, we use trip history data from the Capital Bikeshare system in the Washington DC area and some additional data sources. The study covers seven important aspects of bikeshare transportation systems, which are respectively trip demand and flow, operating activities, use and idle times, trip purpose, origin-destination flows, mobility, and safety. For these aspects, by using appropriate statistical methods and geographic techniques, we investigate travel patterns and characteristics of BSS from data to evaluate the qualitative and quantitative impacts of the inputs from key stakeholders on main measures of effectiveness such as trip costs, mobility, safety, quality of service, and operational efficiency, where key stakeholders include road users, system operators, and city. We also disclose some new patterns and characteristics of BSS to advance the knowledge on travel behaviors. Finally, we briefly summarize our findings and discuss the implications of the patterns and characteristics for data-driven decision supports from the relations between BSS and key stakeholders for promoting bikeshare utilization and transforming urban transportation to be more sustainable.
Road Safety Analysis: Montgomery County, MD |
|---|
In this work, we analyze road safety with an integration of multiple data sources on multiple scales. As a case study, we consider three datasets, including the nationwide Fatality Analysis Reporting System (FARS), the statewide traffic crashes in Maryland (MDCrash), and the countywide traffic violations in Montgomery County, MD (MoCoVio).
- “Multiscale crash analysis: A case study of integrating FARS, Maryland’s crash data, and Montgomery County’s traffic violation data,” in Transportation Research Board (TRB) Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, 2018.
![[PDF]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/lnk.png)
![[Bibtex]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/bib.png)
@InProceedings{xie2018multiscale, title={Multiscale crash analysis: A case study of integrating {FARS}, {Maryland}'s crash data, and {Montgomery County}'s traffic violation data}, author={Xie, Xiao-Feng and Wang, Zun-Jing}, Booktitle = {Transportation Research Board (TRB) Annual Meeting}, number={18-2283}, Address = {Washington, DC}, LNK={https://trid.trb.org/View/1495254}, PDF={http://www.wiomax.com/team/xie/paper/TRB18.pdf}, year={2018} }
 We explore practical values of the multiple data integration on road crash analysis. The crash risk patterns extracted from data fusion is shown to be rather valuable. By identifying determinant risk factors in the patterns, we can better understand the effects of other risk factors. In addition, conditional risk matrix can be computed from data integration to measure the probability of the injury levels and to evaluate the impact of each individual risk factor on injuries. Finally, we conduct a multi-source data integration to discover the safety factors for pedestrians, where we obtain temporal patterns from FARS but acquire spatial patterns from the traffic crash and violation data. The results indicate that, in comparison with only using FARS, integrating multiple data has the power of showing more insights of the patterns on risk factors for traffic crashes, which allows us to not only better optimize limited resources but also realize more effective countermeasures for enhancing road safety.
We explore practical values of the multiple data integration on road crash analysis. The crash risk patterns extracted from data fusion is shown to be rather valuable. By identifying determinant risk factors in the patterns, we can better understand the effects of other risk factors. In addition, conditional risk matrix can be computed from data integration to measure the probability of the injury levels and to evaluate the impact of each individual risk factor on injuries. Finally, we conduct a multi-source data integration to discover the safety factors for pedestrians, where we obtain temporal patterns from FARS but acquire spatial patterns from the traffic crash and violation data. The results indicate that, in comparison with only using FARS, integrating multiple data has the power of showing more insights of the patterns on risk factors for traffic crashes, which allows us to not only better optimize limited resources but also realize more effective countermeasures for enhancing road safety.
Taxi Data Analysis for Urban Mobility & City Dynamics: Washington DC |
|---|
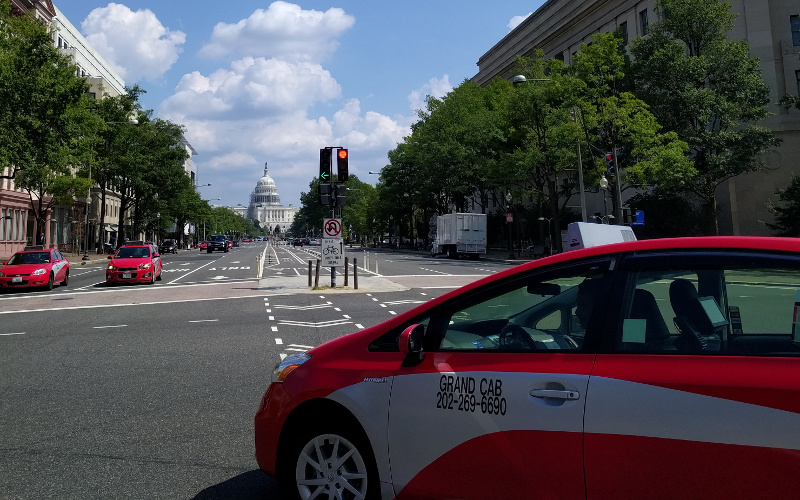 We perform a systematic analysis on the large-scale taxi trip data to uncover urban mobility and city dynamics in multimodal urban transportation environments. As a case study, we use the taxi origin-destination trip data and some additional data sources in Washington DC area. We first study basic characteristics of taxi trips, then focus on five important aspects. Three of them concern urban mobility, which are respectively mobility and cost including effect of traffic congestion, trip safety, and multimodal connectivity; the other two pertain to city dynamics, which are respectively transportation resilience and the relation between trip patterns and land use. For these aspects, we use appropriate statistical methods and geographic techniques to mine patterns and characteristics from taxi trip data for better understanding qualitative and quantitative impacts of the inputs from key stakeholders on available measures of effectiveness on urban mobility and city dynamics, where key stakeholders include road users, system operators, and city. Finally, we briefly summarize our findings and discuss some critical roles and implications of the uncovered patterns and characteristics from the relation between taxi system and key stakeholders. The results can support road users by providing evidence-based information of trip cost, mobility, safety, multimodal connectivity and transportation resilience, can assist taxi drivers and operators to deliver transportation services in a higher quality of mobility, safety and operational efficiency, and can also help city planners and policy makers to transform multimodal transportation and to manage urban resources in a more effective and better way.
We perform a systematic analysis on the large-scale taxi trip data to uncover urban mobility and city dynamics in multimodal urban transportation environments. As a case study, we use the taxi origin-destination trip data and some additional data sources in Washington DC area. We first study basic characteristics of taxi trips, then focus on five important aspects. Three of them concern urban mobility, which are respectively mobility and cost including effect of traffic congestion, trip safety, and multimodal connectivity; the other two pertain to city dynamics, which are respectively transportation resilience and the relation between trip patterns and land use. For these aspects, we use appropriate statistical methods and geographic techniques to mine patterns and characteristics from taxi trip data for better understanding qualitative and quantitative impacts of the inputs from key stakeholders on available measures of effectiveness on urban mobility and city dynamics, where key stakeholders include road users, system operators, and city. Finally, we briefly summarize our findings and discuss some critical roles and implications of the uncovered patterns and characteristics from the relation between taxi system and key stakeholders. The results can support road users by providing evidence-based information of trip cost, mobility, safety, multimodal connectivity and transportation resilience, can assist taxi drivers and operators to deliver transportation services in a higher quality of mobility, safety and operational efficiency, and can also help city planners and policy makers to transform multimodal transportation and to manage urban resources in a more effective and better way.
- “Uncovering Urban Mobility and City Dynamics from Large-Scale Taxi Origin-Destination (O-D) Trips: Case Study in Washington DC Area,” WIOMAX, WIO-TR-18-003, 2018.
![[PDF]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/pdf.png)
![[DOI]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/doi.png)
![[Bibtex]](http://www.wiomax.com/wp-content/plugins/papercite/img/bib.png)
@TechReport{xie2018uncovering, title = {Uncovering Urban Mobility and City Dynamics from Large-Scale Taxi Origin-Destination ({O-D}) Trips: Case Study in {Washington DC} Area}, author = {Xiao-Feng Xie and Wang, Zunjing Jenipher}, year = {2018}, number = {WIO-TR-18-003}, Institution={WIOMAX}, PDF = {http://www.wiomax.com/doc/report/WIO-TR-18-003.pdf}, DOI = {10.13140/RG.2.2.32170.72644}, urldate = {2018-07-25}, upddate = {2018-07-25} }
WIOMAX is a research and consulting team to explore real-time, smart and scalable solutions especially for applications to achieve Smart Mobility and Smart Cities by integrating cutting-edge DOAI [Data Analytics + Optimization + Artificial Intelligence (AI) + Internet of Things (IoT)] technologies, from basic research to industry transition and product development and support.
